In today’s evolving technological landscape, security remains a major concern across various domains. From public security and immigration management to mobile payment systems and business operations, the need to accurately identify and authenticate individuals is crucial.
Biometric identification has emerged as a revolutionary solution to this challenge, offering enhanced security and convenience. Among the array of biometric features, palm biometric identification, encompassing both palmprints and palm vein recognition, stands out as a promising avenue. This article delves into the world of palm biometric identification, exploring its technology, applications, advantages, challenges, and its potential to reshape the future of authentication.
Understanding Palm Biometric Identification
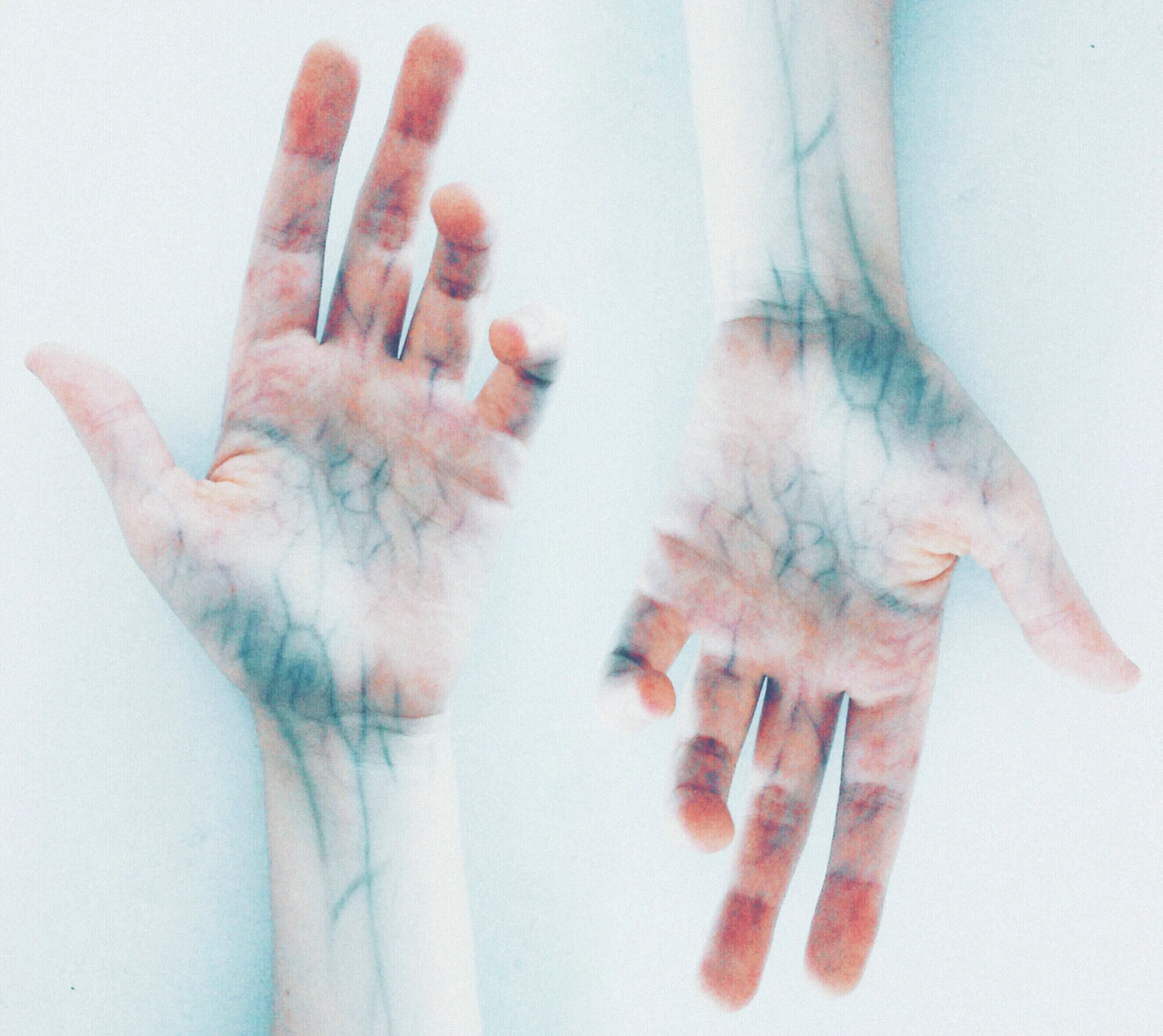
Palm biometric identification leverages the distinctive patterns present in an individual’s palm as a means of personal authentication. This technology relies on the inherent uniqueness of palmprints and palm veins, capturing and analyzing these patterns to verify identity. Unlike traditional authentication methods such as PINs, signatures, or passwords, palm biometric identification offers a more robust and secure solution.
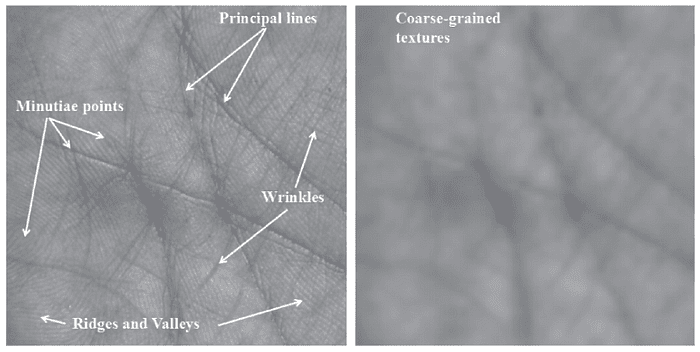
Palm print recognition relies on the unique characteristics found in the palm of an individual’s hand. These systems employ scanning devices or camera-based applications, coupled with specialized software, to analyze photographic images of a person’s palm and compare them to stored records.
Similar to fingerprint recognition, palm print recognition utilizes various methods such as optical, thermal, or tactile approaches to capture detailed patterns, including ridges, bifurcations, scars, creases, and texture on the palm’s surface. Some palm scanners require physical contact with a screen, while others operate in a contactless manner.
Palm print and fingerprint recognition are often used in conjunction to bolster identification accuracy. Since a handprint covers a larger skin area and provides more identifying information, it significantly reduces the chances of false positives and makes deliberate falsification considerably more challenging.
Palmprints and Palm Veins: A Dual Authentication Approach
The field of palm biometric identification encompasses both palmprints and palm veins. Palmprints involve capturing the intricate lines, wrinkles, and epidermal ridges present on an individual’s palm. These patterns, unique to each individual, contain a wealth of information that contributes to accurate identification. Palm vein recognition, on the other hand, delves deeper by utilizing near-infrared (NIR) light to capture the distinct vein patterns beneath the palm’s surface. The deoxygenated blood in the veins absorbs NIR light, creating a pattern that is difficult to replicate. This subcutaneous feature enhances security, making it challenging for fraudsters to imitate.
When an individual places their palm on the scanner again, the system compares the newly captured pattern with the stored data in the database to verify identity. This process offers both accuracy and security, ensuring that only the authorized individual gains access.
Applications of Palm Biometric Identification
The versatility of palm biometric identification is evident through its myriad applications across various sectors:
- Personal Identification: Palm biometrics provides a higher level of accuracy compared to methods like facial recognition or fingerprints. Its comprehensive pattern capture ensures reliable identification.
- Access Control: Palm biometrics offers enhanced security for access control, surpassing the vulnerabilities of traditional password-based systems.
- Healthcare: In the medical field, palm vein scans can be linked to patient medical histories, expediting identification and information retrieval.
- Banking: Palm vein recognition can serve as a secure digital signature for financial transactions, mitigating the risk of fraud.
- Payment: Palm biometric identification is revolutionizing the payment industry. It provides a secure and convenient method for authenticating transactions. Users can complete payments by simply scanning their palm, reducing the need for traditional PINs or signatures and enhancing security in online and offline financial operations.
The application of palm biometric identification extends beyond the examples mentioned above, being relevant wherever specific conditions are met:
- Clean Acquisition Environment: Palm biometric identification thrives in well-maintained surroundings where hands are clearly visible and clean. It’s most effective when readers are not exposed to severe damaging conditions.
- Exposed Hand Parts: In situations where individuals wear permanent hand coverings or protection, conducting palm biometric identification becomes challenging due to the obstruction of the palm.
- Cost Considerations: The implementation of palm biometric identification may also be influenced by cost factors, encompassing expenses related to acquisition hardware and the processing of biometric data.
Advantages of Palm Biometric Identification
- Unmatched Security: Palm biometric identification offers a higher level of security than many other biometric methods. The unique vein patterns are difficult to replicate, making it resistant to spoofing attacks.
- Privacy: Unlike facial recognition, palm patterns cannot be captured from a distance without the individual’s consent, minimizing privacy concerns.
- Accuracy and Reliability: The larger size of palm patterns compared to fingerprints or iris scans enhances identification accuracy, reducing false rejections.
- Consistency: Unlike other biometric features that might change over time, palm vein patterns remain consistent throughout an individual’s life.
- Hygiene: The contactless nature of palm vein scanning enhances hygiene, especially in environments with high footfall.
Addressing Challenges and Advancing Palm Biometric Technologies
Despite its promising potential, palm biometric identification faces certain challenges as :
- Anti-Spoofing Capability: As with any biometric method, the technology must be safeguarded against spoofing attacks. Research is ongoing to enhance the anti-spoofing capability of palm veins.
- Cost Considerations: The initial cost of implementing palm biometric systems can be high. However, this cost is expected to decrease as the technology becomes more widespread.
Future Outlook and Conclusion
Biometric identification, particularly palm biometrics, is at the forefront of the future of security. Its remarkable blend of security, precision, and ease makes it a fundamental part of upcoming authentication systems. As technology evolves and research advances, the challenges linked to palm biometrics will likely be resolved, paving the way for broader use. With the potential to transform personal ID, simplify business tasks, and fortify security across sectors, palm biometrics is set to redefine how we authenticate, guaranteeing a safer and more convenient future.






