As our world becomes increasingly digital, the convenience of online transactions has become an integral part of everyday life. However, this convenience comes with a downside: the growing threat of online fraud. Cybercriminals are constantly evolving their tactics, making it imperative for both consumers and businesses to stay ahead of the curve.
In this context, ensuring the security of online transactions has never been more crucial. It’s not just about protecting money; it’s about maintaining trust in the digital economy.
This is where the Observatoire de la sécurité des moyens de paiement (OSMP) steps in. Tasked with safeguarding the integrity of payment methods in France, OSMP has been at the forefront of efforts to enhance security standards. In response to the evolving threat landscape, OSMP has rolled out a comprehensive plan designed to bolster the security of remote card payments, ensuring that consumers can continue to enjoy the benefits of online transactions with peace of mind.
Understanding OSMP: Role and Responsibilities
The Observatoire de la sécurité des moyens de paiement (OSMP) is a key player in France’s financial ecosystem, responsible for monitoring and enhancing the security of various payment methods. Established by the “Loi Sapin 2” on December 9, 2016, OSMP expanded the mandate of its predecessor, the Observatoire de la sécurité des cartes de paiement, which was originally focused solely on payment cards. Today, OSMP’s scope covers all scriptural payment methods, reflecting the broadening landscape of financial transactions in the digital age.

Origins and Evolution
OSMP was created in response to the need for a more comprehensive approach to payment security. As the digital economy grew, so did the variety of payment methods, from traditional cards to electronic money and direct debits. Recognizing this shift, the French government expanded the role of the original observatory to cover the entire spectrum of scriptural payments. This evolution has enabled OSMP to address the diverse challenges posed by modern payment systems.
Core Missions
OSMP’s responsibilities are multi-faceted, focusing on three main areas:
- Strengthening Payment Security: OSMP monitors the implementation of security measures across the payment ecosystem. This includes working with issuers, merchants, and companies to ensure that robust security protocols are in place and adhered to.
- Compiling Fraud Statistics: By collecting data from payment issuers, OSMP establishes and analyzes statistics related to payment fraud. This data is crucial for understanding trends and developing strategies to combat fraud. Additionally, OSMP provides recommendations to standardize the calculation of fraud rates across different payment methods.
- Technological Surveillance: OSMP stays ahead of the curve by conducting technological surveillance in the field of payment methods. This involves monitoring developments that could affect payment security and proposing solutions to mitigate emerging threats. OSMP also facilitates the exchange of information among its members, ensuring that all stakeholders are equipped with the latest knowledge while maintaining confidentiality where necessary.
Legal Framework
The legal foundations of OSMP are enshrined in the Code monétaire et financier (CMF), which outlines its missions and organizational structure:
- Missions: Defined under Article L141-4 of the CMF.
- Composition and Organization: Detailed in Articles R142-22 to R142-27 of the CMF.
OSMP’s membership is composed of various stakeholders, including government representatives, members of the financial sector, and independent experts. These members are appointed for renewable three-year terms, ensuring continuity and the inclusion of diverse perspectives in decision-making.
In essence, OSMP plays a critical role in maintaining the security and trustworthiness of France’s payment systems. As digital transactions continue to evolve, so too does the scope and importance of OSMP’s work, positioning it as a central figure in the fight against payment fraud.
The Action Plan: Enhancing Security for Remote Card Payments
In response to the growing challenges of online fraud, the Observatoire de la sécurité des moyens de paiement (OSMP) has developed a robust action plan to enhance the security of remote card payments. This plan is designed to mitigate risks by implementing targeted measures that protect both consumers and businesses, while also ensuring that e-commerce remains a viable and secure avenue for transactions.
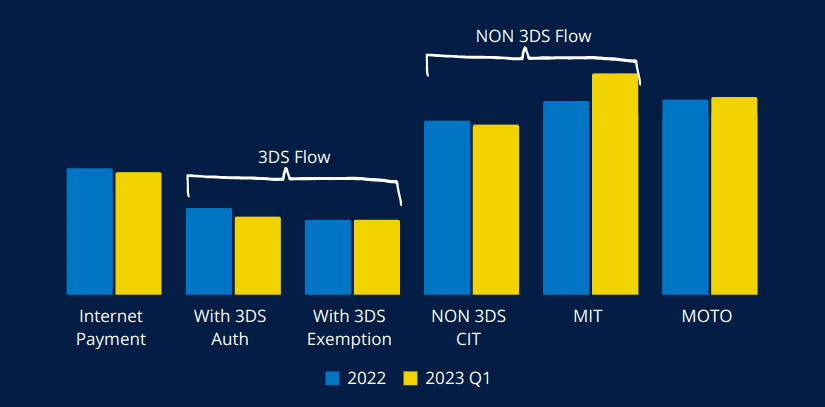
Key Objectives
The primary goal of OSMP’s action plan is to reduce the incidence of fraud in remote card payments, particularly in scenarios where strong customer authentication (SCA) is not used. By focusing on high-risk transactions, the plan aims to strike a balance between security and usability, ensuring that legitimate transactions are not unduly hindered while fraudulent activities are effectively curtailed.
This initiative reflects OSMP’s commitment to maintaining the integrity of France’s payment systems in an increasingly digital world. By setting clear objectives and implementing phased changes, OSMP is paving the way for a more secure online payment environment.
Phased Implementation
One of the key components of OSMP’s plan is the phased reduction of velocity thresholds. Velocity limits refer to caps on the number or value of non-authenticated transactions that can occur within a certain period (24h). These limits are set to gradually decrease over time, allowing the market to adapt while steadily tightening security.
The implementation timeline is structured to ensure that each phase is manageable for all stakeholders. For example, the initial threshold might be set at €500, which would then be reduced to €250 and finally to €100. This gradual approach helps businesses and consumers adjust to the new rules without causing significant disruption to e-commerce operations.

OSMP will monitor the effects of each phase closely, ensuring that the reduction in thresholds does not negatively impact the functionality of online payment systems. By doing so, OSMP can make any necessary adjustments to maintain a balance between security and user experience.
3-D Secure Protocol
A critical aspect of the action plan is the promotion of the 3-D Secure protocol. This protocol, which provides an additional layer of authentication during online transactions, is central to OSMP’s strategy for enhancing payment security.
3-D Secure requires customers to verify their identity during transactions, typically by entering a one-time password (OTP) sent to their mobile device. This process helps ensure that the person making the transaction is indeed the cardholder, significantly reducing the likelihood of fraudulent activity.
OSMP’s plan encourages businesses to adopt 3-D Secure, particularly for high-value transactions or those deemed to be at greater risk of fraud. By increasing the use of this protocol, OSMP aims to reduce the overall vulnerability of remote card payments and foster a more secure e-commerce environment.
Velocity Limits: A New Approach to Risk Management
As part of its comprehensive action plan, OSMP has introduced velocity limits as a proactive measure to combat fraud in remote card payments. These limits are designed to cap the frequency and value of non-authenticated transactions, thereby reducing the opportunities for fraudulent activities to occur.
What Are Velocity Limits?
Velocity limits function as a safeguard by restricting the number or total value of transactions that can be processed within a specified timeframe (24h) without triggering additional security checks. These limits are particularly effective in preventing fraud patterns where multiple unauthorized transactions are made within a short period.
For instance, if a fraudster gains access to a payment card and attempts to make several purchases quickly, velocity limits would halt these transactions once the threshold is exceeded. This not only protects the cardholder but also mitigates potential losses for merchants.
Phased Reductions
The introduction of velocity limits is being implemented in phases, with initial thresholds set at a level that allows the market to adapt while still enhancing security. For example, the plan may start with a velocity limit of €500 per day for non-authenticated transactions. As the market adjusts, this threshold will be gradually reduced to €250, and eventually to €100.
This phased approach ensures that businesses and consumers are not overwhelmed by sudden changes, while still achieving the plan’s ultimate goal of heightened security. By steadily lowering the thresholds, OSMP aims to incrementally reduce the risk of fraud while giving all parties time to adapt to the new rules.
Impact on Merchants and Consumers
For merchants, the implementation of velocity limits necessitates a review of their current payment processing practices. Businesses will need to ensure that they can handle the new limits without negatively impacting legitimate transactions. This might involve encouraging customers to use payment methods that support strong customer authentication or integrating additional security measures into their payment processes.
Consumers, on the other hand, may notice changes in how their online transactions are processed, especially if they frequently make purchases that fall close to the new velocity limits. While these changes might require some adjustment, the increased security they provide will ultimately protect consumers from potential fraud.
The Role of 3-D Secure in Strengthening Payment Security
What is 3-D Secure?
3-D Secure is an authentication protocol designed to provide an additional layer of security for online credit and debit card transactions. Originally developed by Visa and branded as “Verified by Visa,” it is now widely adopted by other card networks under various names, such as “Mastercard SecureCode” and “American Express SafeKey.”
The “3-D” in 3-D Secure refers to the “Three-Domain” model, which includes:
- The Merchant Domain: The retailer or service provider where the transaction is taking place.
- The Issuer Domain: The bank that issued the card being used for the transaction.
- The Interoperability Domain: The infrastructure that supports the secure processing of the transaction.
When a customer initiates a transaction with 3-D Secure, they are prompted to authenticate themselves, usually via a one-time password (OTP) sent to their mobile device or through biometric methods. This step helps ensure that the person making the transaction is indeed the legitimate cardholder.
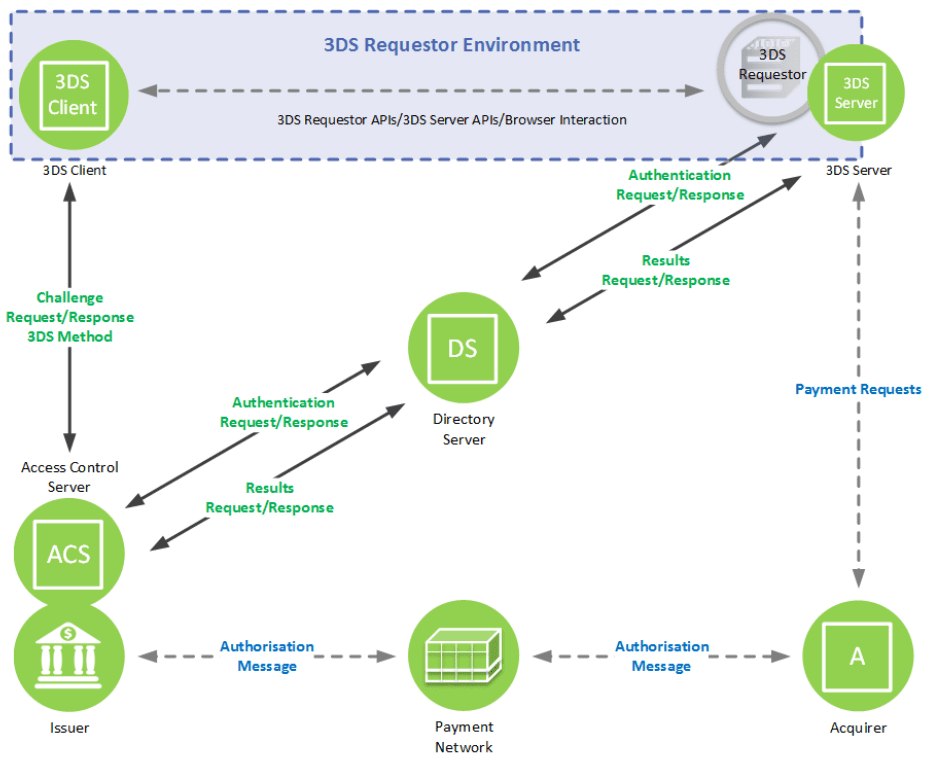
Benefits of 3-D Secure
The primary benefit of 3-D Secure is its ability to significantly reduce the risk of fraud in online transactions. By adding an extra step of authentication, it becomes much more difficult for fraudsters to use stolen card information for unauthorized purchases. This not only protects consumers but also reduces the liability for merchants and card issuers.
Moreover, 3-D Secure enhances consumer trust. Knowing that their transactions are protected by additional security measures can make customers more comfortable making purchases online, which is particularly important in an era where data breaches and online scams are a growing concern.
OSMP’s Push for Adoption
Recognizing the effectiveness of 3-D Secure, OSMP is actively encouraging its adoption across the e-commerce sector. As part of its action plan, OSMP is promoting the integration of 3-D Secure, especially for high-risk transactions or those that exceed the newly introduced velocity limits.
OSMP’s strategy includes providing guidance and resources to merchants to facilitate the implementation of 3-D Secure. This might involve technical support, best practice recommendations, and collaboration with payment service providers to ensure a smooth transition. The goal is to make 3-D Secure a standard part of the online shopping experience in France, thereby enhancing overall payment security.
The Future of Online Payment Security in France
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, so too must the strategies for protecting online transactions. The Observatoire de la sécurité des moyens de paiement (OSMP) is at the forefront of this effort in France, ensuring that the country’s payment systems are equipped to handle the challenges of the future. This final chapter looks ahead to what the future holds for online payment security and how OSMP is preparing for it.
Adapting to Emerging Technologies
One of the key challenges in online payment security is the rapid pace of technological change. New payment methods, such as digital wallets, cryptocurrency, and even biometric payments, are becoming increasingly popular. While these technologies offer convenience, they also present new security risks that need to be addressed.
OSMP is committed to staying ahead of these trends by continuously updating its security guidelines and recommendations. This includes conducting research into emerging technologies and assessing their potential impact on payment security. By doing so, OSMP ensures that France’s payment systems remain secure and resilient, even as new forms of payment become mainstream.
Collaborative Approach to Security
The future of online payment security will depend heavily on collaboration between various stakeholders, including government agencies, financial institutions, merchants, and technology providers. OSMP plays a central role in facilitating this collaboration, bringing together diverse perspectives to develop comprehensive security strategies.
This collaborative approach is particularly important as cybercriminals become more sophisticated and organized. By working together, stakeholders can share information, identify emerging threats, and develop coordinated responses that protect the entire payment ecosystem.
Regulatory Evolution
As part of its ongoing efforts to enhance payment security, OSMP is also involved in shaping regulatory policies that govern online transactions. This involves working closely with national and European regulators to ensure that security measures are not only effective but also aligned with broader legal frameworks.
Future regulatory developments may include stricter requirements for strong customer authentication, enhanced data protection measures, and new standards for emerging payment technologies. OSMP’s proactive involvement in these discussions ensures that France remains at the cutting edge of payment security regulation.
Continuous Improvement
OSMP’s approach to online payment security is rooted in the principle of continuous improvement. The organization recognizes that the fight against fraud is ongoing and that security measures must evolve to keep pace with new threats. This means regularly reviewing and updating its action plan, incorporating feedback from the market, and adapting to changes in the digital landscape.
Looking forward, OSMP is committed to maintaining the trust and security of France’s payment systems. By fostering innovation, promoting best practices, and ensuring a robust regulatory environment, OSMP is helping to build a secure foundation for the future of online payments.
Conclusion: A Secure Path Forward
As online transactions become an ever more integral part of our daily lives, the importance of secure payment systems cannot be overstated. OSMP’s comprehensive action plan represents a significant step forward in protecting remote card payments from fraud, while its ongoing efforts ensure that France is well-prepared for the challenges of tomorrow.
Through initiatives like the phased implementation of velocity limits, the promotion of 3-D Secure, and the continuous monitoring and adjustment of security measures, OSMP is laying the groundwork for a safer, more secure digital economy. As the landscape of online payments continues to evolve, OSMP’s commitment to security will remain a cornerstone of its mission, ensuring that both businesses and consumers can engage in e-commerce with confidence.






